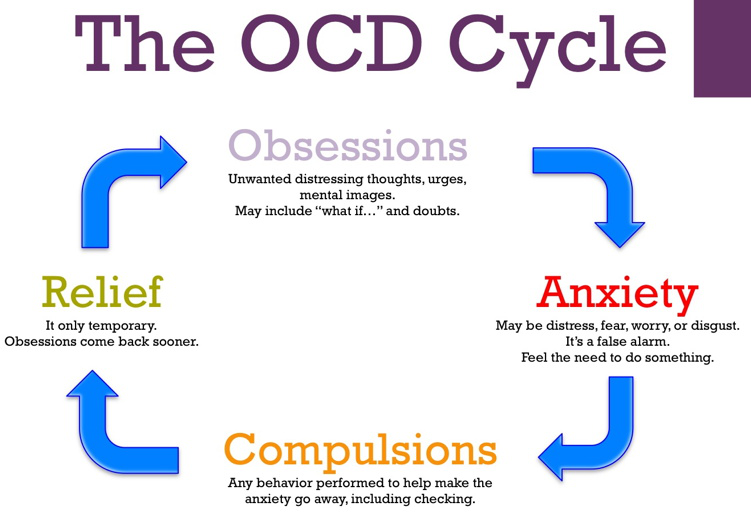
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) therapy is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that is effective in treating anxiety disorders, particularly Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Here is a general outline for planning ERP therapy sessions:
- Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the client’s symptoms and their specific triggers. Develop a hierarchy of feared situations or objects, ranging from least to most anxiety-provoking.
- Education: Educate the client about the nature of their anxiety disorder and how ERP therapy can help them overcome their symptoms.
- Setting Goals: Set specific goals for each session and establish a treatment plan that outlines the steps the client will take to overcome their anxiety.
- Session Structure: Structure each session to include exposure exercises, relaxation techniques, and cognitive restructuring exercises.
- Exposure Exercises: Gradually expose the client to the feared situations or objects, starting with the least anxiety-provoking situation and moving up the hierarchy.
- Response Prevention: During the exposure exercises, prevent the client from engaging in their usual compulsive behaviors (such as washing or checking) that they use to reduce their anxiety.
- Relaxation Techniques: Teach the client relaxation techniques (such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation) to help them cope with their anxiety during the exposure exercises.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Help the client to identify and challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs about their anxiety and the feared situations.
- Homework Assignments: Assign homework exercises for the client to practice between sessions, including exposure exercises and relaxation techniques.
- Review: Review progress with the client at the end of each session, and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
It is important to note that ERP therapy should be conducted under the guidance of a trained therapist who can tailor the treatment plan to the individual needs of the client.



Leave a Reply